SR Bearings (ตลับลูกปืน LM Guide SR, which is the term in Thai) are a part that isn’t visible, tend to go about their business in the background, and are usually given little attention. To help you move, and more significantly, move quickly, they are an essential but frequently disregarded component.
You don’t need to give more to the wheel bearings when shopping for sleek, aero-carbon wheels. However, they are among the most essential parts of your wheel, and we at Scribe have given them much attention.
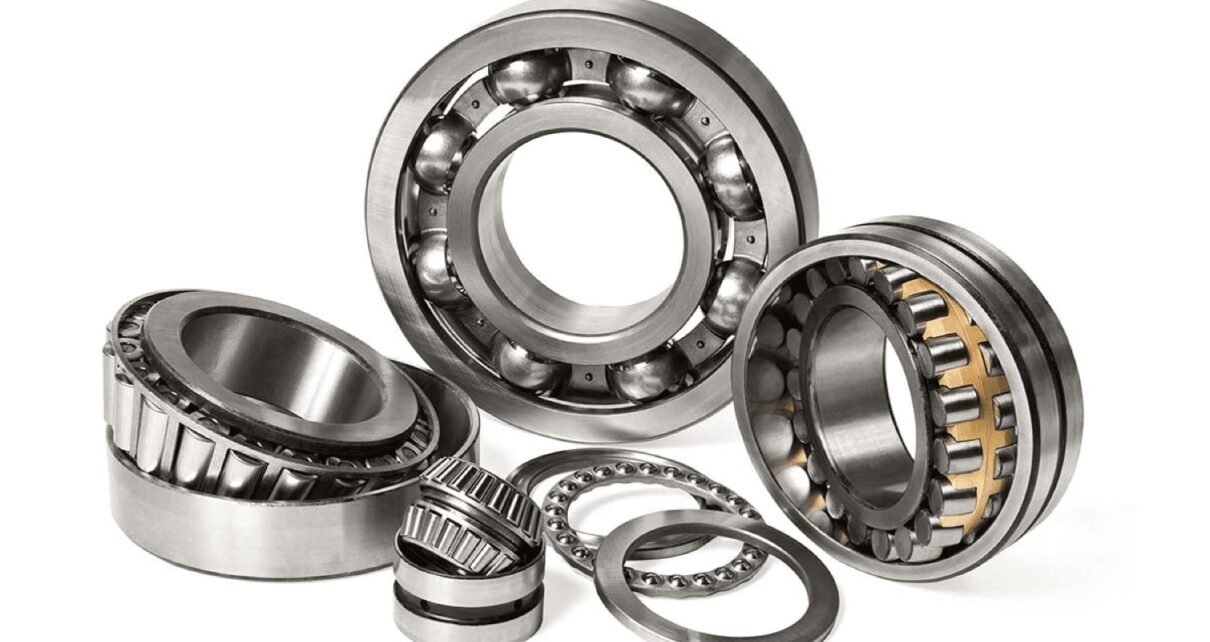
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
The ball and the ring form a contact angle. Contact angles of 15, 30, and 40 degrees are the industry standard. Axial load capacity increases as the contact angle is more significant. When the contact angle is minimal, high-speed spinning is easier. Support axial load in one direction and radial load in the other. The rear structure consists of two single-row angular contact ball bearings supporting radial and bidirectional axial loads since they share the inner and outer rings.
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Auto-adjusting for shaft misalignment due to shaft deflection or casing misalignment, the outer ring raceway’s double-row steel balls are of the inner spherical type. Attaching the tapered hole bearing to the shaft is a breeze with the help of fasteners. Take radial strains.
Spherical Roller Bearings
This bearing type features spherical rollers between the outer and inner rings of the double raceway. It is classified into four kinds—R, RH, RHA, and SR—based on the various internal structures. Radial and bidirectional axial loads can be accommodated by the self-aligning capability of the consistent centre of the bearing, which allows it to automatically correct shaft misalignment due to deflection or misalignment of the casing.
Thrust Spherical Roller Bearings
An oblique arrangement of spherical rollers characterizes this bearing type. The self-aligning performance and spherical raceway surface allow the shaft to be slightly angled, and the axial load capacity is enormous. When it comes to radial loads, oil lubrication is typically employed.
Tapered Roller Bearings
The broad rib of the inner ring guides the truncated rollers in this bearing design. By design, the conical surfaces of the roller rolling surface, the outer ring raceway surface, and the inner ring raceway surface’s vertex all meet at the bearing’s centerline. Double-row bearings are the way to go when it comes to bearing large and impact loads, while single-row bearings are only suitable for radial and one-way axial loads.
Thrust Ball Bearings
A cage assembly, a ball, and a raceway ring fashioned like a washer make up its components. One raceway ring is termed a shaft washer, which is matched with the shaft; another is called a seat ring, which is matched with the housing. While both types of bearings can support axial loads in one direction, the two-way bearing is well suited for use with the secret shaft in the centre ring. On the other hand, neither type of bearing is suitable for use with radial loads.